Baeldung Pro comes with both absolutely No-Ads as well as finally with Dark Mode, for a clean learning experience:
Once the early-adopter seats are all used, the price will go up and stay at $33/year.
In this tutorial, we’ll cover the implementation of a binary tree in Java.
For the sake of this tutorial, we’ll use a sorted binary tree that contains int values.
A binary tree is a recursive data structure where each node can have 2 children at most.
A common type of binary tree is a binary search tree, in which every node has a value that is greater than or equal to the node values in the left sub-tree, and less than or equal to the node values in the right sub-tree.
Here’s a visual representation of this type of binary tree:
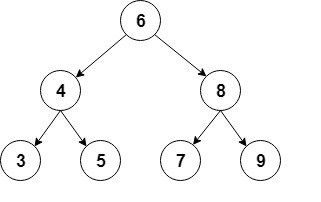
For the implementation, we’ll use an auxiliary Node class that will store int values, and keep a reference to each child:
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
right = null;
left = null;
}
}Then we’ll add the starting node of our tree, usually called the root:
public class BinaryTree {
Node root;
// ...
}Now let’s see the most common operations we can perform on a binary tree.
The first operation we’re going to cover is the insertion of new nodes.
First, we have to find the place where we want to add a new node in order to keep the tree sorted. We’ll follow these rules starting from the root node:
Then we’ll create a recursive method to do the insertion:
private Node addRecursive(Node current, int value) {
if (current == null) {
return new Node(value);
}
if (value < current.value) {
current.left = addRecursive(current.left, value);
} else if (value > current.value) {
current.right = addRecursive(current.right, value);
} else {
// value already exists
return current;
}
return current;
}Next we’ll create the public method that starts the recursion from the root node:
public void add(int value) {
root = addRecursive(root, value);
}Let’s see how we can use this method to create the tree from our example:
private BinaryTree createBinaryTree() {
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.add(6);
bt.add(4);
bt.add(8);
bt.add(3);
bt.add(5);
bt.add(7);
bt.add(9);
return bt;
}Now let’s add a method to check if the tree contains a specific value.
As before, we’ll first create a recursive method that traverses the tree:
private boolean containsNodeRecursive(Node current, int value) {
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
if (value == current.value) {
return true;
}
return value < current.value
? containsNodeRecursive(current.left, value)
: containsNodeRecursive(current.right, value);
}Here we’re searching for the value by comparing it to the value in the current node; we’ll then continue in the left or right child depending on the outcome.
Next we’ll create the public method that starts from the root:
public boolean containsNode(int value) {
return containsNodeRecursive(root, value);
}Then we’ll create a simple test to verify that the tree really contains the inserted elements:
@Test
public void givenABinaryTree_WhenAddingElements_ThenTreeContainsThoseElements() {
BinaryTree bt = createBinaryTree();
assertTrue(bt.containsNode(6));
assertTrue(bt.containsNode(4));
assertFalse(bt.containsNode(1));
}All the nodes added should be contained in the tree.
Another common operation is the deletion of a node from the tree.
First, we have to find the node to delete in a similar way as before:
private Node deleteRecursive(Node current, int value) {
if (current == null) {
return null;
}
if (value == current.value) {
// Node to delete found
// ... code to delete the node will go here
}
if (value < current.value) {
current.left = deleteRecursive(current.left, value);
return current;
}
current.right = deleteRecursive(current.right, value);
return current;
}Once we find the node to delete, there are 3 main different cases:
Let’s see how we would implement the first case when the node is a leaf node:
if (current.left == null && current.right == null) {
return null;
}Now let’s continue with the case when the node has one child:
if (current.right == null) {
return current.left;
}
if (current.left == null) {
return current.right;
}Here we’re returning the non-null child so it can be assigned to the parent node.
Finally, we have to handle the case where the node has two children.
First, we need to find the node that will replace the deleted node. We’ll use the smallest node of the soon to be deleted node’s right sub-tree:
private int findSmallestValue(Node root) {
return root.left == null ? root.value : findSmallestValue(root.left);
}Then we assign the smallest value to the node to delete, and after that, we’ll delete it from the right sub-tree:
int smallestValue = findSmallestValue(current.right);
current.value = smallestValue;
current.right = deleteRecursive(current.right, smallestValue);
return current;Finally, we’ll create the public method that starts the deletion from the root:
public void delete(int value) {
root = deleteRecursive(root, value);
}Now let’s check that the deletion worked as expected:
@Test
public void givenABinaryTree_WhenDeletingElements_ThenTreeDoesNotContainThoseElements() {
BinaryTree bt = createBinaryTree();
assertTrue(bt.containsNode(9));
bt.delete(9);
assertFalse(bt.containsNode(9));
}In this section, we’ll explore different ways of traversing a tree, covering in detail the depth-first and breadth-first searches.
We’ll use the same tree that we used before, and we’ll examine the traversal order for each case.
Depth-first search is a type of traversal that goes deep as much as possible in every child before exploring the next sibling.
There are several ways to perform a depth-first search: in-order, pre-order and post-order.
The in-order traversal consists of first visiting the left sub-tree, then the root node, and finally the right sub-tree:
public void traverseInOrder(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
traverseInOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(" " + node.value);
traverseInOrder(node.right);
}
}If we call this method, the console output will show the in-order traversal:
3 4 5 6 7 8 9Pre-order traversal visits first the root node, then the left sub-tree, and finally the right sub-tree:
public void traversePreOrder(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(" " + node.value);
traversePreOrder(node.left);
traversePreOrder(node.right);
}
}Let’s check the pre-order traversal in the console output:
6 4 3 5 8 7 9Post-order traversal visits the left sub-tree, the right subt-ree, and the root node at the end:
public void traversePostOrder(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
traversePostOrder(node.left);
traversePostOrder(node.right);
System.out.print(" " + node.value);
}
}Here are the nodes in post-order:
3 5 4 7 9 8 6This is another common type of traversal that visits all the nodes of a level before going to the next level.
This kind of traversal is also called level-order, and visits all the levels of the tree starting from the root, and from left to right.
For the implementation, we’ll use a Queue to hold the nodes from each level in order. We’ll extract each node from the list, print its values, then add its children to the queue:
public void traverseLevelOrder() {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
nodes.add(root);
while (!nodes.isEmpty()) {
Node node = nodes.remove();
System.out.print(" " + node.value);
if (node.left != null) {
nodes.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodes.add(node.right);
}
}
}In this case, the order of the nodes will be:
6 4 8 3 5 7 9In this article, we learned how to implement a sorted binary tree in Java, and its most common operations.