Baeldung Pro comes with both absolutely No-Ads as well as finally with Dark Mode, for a clean learning experience:
Once the early-adopter seats are all used, the price will go up and stay at $33/year.
Last updated: April 17, 2025
Simply put, before we can work with an object on the JVM, it has to be initialized.
In this tutorial, we’ll examine the various ways we can initialize primitive types and objects.
Let’s start by making sure that we’re on the same page.
Declaration is the process of defining the variable, along with its type and name.
Here we’re declaring the id variable:
int id;Initialization, on the other hand, is all about assigning a value:
id = 1;To demonstrate, we’ll create a User class with a name and id properties:
public class User {
private String name;
private int id;
// standard constructor, getters, setters,
}Next, we’ll see that initialization works differently depending on the type of field we’re initializing.
Java provides two types of data representation: primitive types and reference types. In this section, we’ll discuss the differences between the two with regards to initialization.
Java has eight built-in data types, referred to as Java primitive types; variables of this type hold their values directly.
Reference types hold references to objects (instances of classes). Unlike primitive types that hold their values in the memory where the variable is allocated, references don’t hold the value of the object they refer to.
Instead, a reference points to an object by storing the memory address where the object is located.
Note that Java doesn’t allow us to discover what the physical memory address is. Rather, we can only use the reference to refer to the object.
Let’s look at an example that declares and initializes a reference type out of our User class:
@Test
public void whenIntializedWithNew_thenInstanceIsNotNull() {
User user = new User();
assertThat(user).isNotNull();
}As we can see, a reference can be assigned to a new object by using the keyword new, which is responsible for creating the new User object.
Let’s continue with learning more about object creation.
Unlike with primitives, objects creation is a bit more complex. This is because we’re not just adding the value to the field; instead, we trigger the initialization using the new keyword. This, in return, invokes a constructor and initializes the object in memory.
Let’s discuss constructors and the new keyword in further detail.
The new keyword is responsible for allocating memory for the new object through a constructor.
A constructor is typically used to initialize instance variables representing the main properties of the created object.
If we don’t supply a constructor explicitly, the compiler will create a default constructor which has no arguments, and just allocates memory for the object.
A class can have many constructors, as long as their parameters lists are different (overload). Every constructor that doesn’t call another constructor in the same class has a call to its parent constructor, whether it was written explicitly or inserted by the compiler through super().
Let’s add a constructor to our User class:
public User(String name, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}Now we can use our constructor to create a User object with initial values for its properties:
User user = new User("Alice", 1);In the following sections, we’ll look at the different types of scopes that a variable in Java can exist within, and how this affects the initialization process.
Instance and class variables don’t require us to initialize them. As soon as we declare these variables, they’re given a default value:
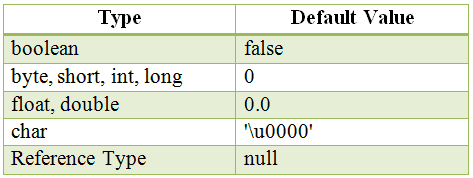
Now let’s try to define some instance and class-related variables, and test whether they have a default value or not:
@Test
public void whenValuesAreNotInitialized_thenUserNameAndIdReturnDefault() {
User user = new User();
assertThat(user.getName()).isNull();
assertThat(user.getId() == 0);
}Local variables must be initialized before use, as they don’t have a default value and the compiler won’t let us use an uninitialized value.
For example, the following code generates a compiler error:
public void print(){
int i;
System.out.println(i);
}The final keyword applied to a field means that the field’s value can no longer be changed after initialization. In this way, we can define constants in Java.
Let’s add a constant to our User class:
private static final int YEAR = 2000;Constants must be initialized either when they’re declared or in a constructor.
In Java, an initializer is a block of code that has no associated name or data type and is placed outside of any method, constructor, or another block of code.
Java offers two types of initializers, static and instance initializers. Let’s see how we can use each of them.
We can use these to initialize instance variables.
To demonstrate, we’ll provide a value for a user id using an instance initializer in our User class:
{
id = 0;
}A static initializer, or static block, is a block of code which is used to initialize static fields. In other words, it’s a simple initializer marked with the keyword static:
private static String forum;
static {
forum = "Java";
}When writing code that initializes different types of fields, we have to keep an eye on the order of initialization.
In Java, the order for initialization statements is as follows:
Now that we’ve learned how to declare and initialize objects, let’s discover what happens to objects when they’re not in use.
Unlike other languages where we have to worry about object destruction, Java takes care of obsolete objects through its garbage collector.
All objects in Java are stored in our program’s heap memory. In fact, the heap represents a large pool of unused memory allocated for our Java application.
On the other hand, the garbage collector is a Java program that takes care of automatic memory management by deleting objects that are no longer reachable.
For a Java object to become unreachable, it has to encounter one of the following situations:
In conclusion, an object is first created from a class, usually using the keyword new. Then the object lives its life, and provides us with access to its methods and fields.
Finally, when it’s no longer needed, the garbage collector destroys it.
In this section, we’ll take a brief look at methods other than the new keyword for creating objects, and learn how to apply them, specifically reflection, cloning, and serialization.
Reflection is a mechanism we can use to inspect classes, fields, and methods at run-time. Here’s an example of creating our User object using reflection:
@Test
public void whenInitializedWithReflection_thenInstanceIsNotNull()
throws Exception {
User user = User.class.getConstructor(String.class, int.class)
.newInstance("Alice", 2);
assertThat(user).isNotNull();
}In this case, we’re using reflection to find and invoke a constructor of the User class.
The next method, cloning, is a way to create an exact copy of an object. For this, our User class must implement the Cloneable interface:
public class User implements Cloneable { //... }Now we can use the clone() method to create a new clonedUser object that has the same property values as the user object:
@Test
public void whenCopiedWithClone_thenExactMatchIsCreated()
throws CloneNotSupportedException {
User user = new User("Alice", 3);
User clonedUser = (User) user.clone();
assertThat(clonedUser).isEqualTo(user);
}We can also use the sun.misc.Unsafe class to allocate memory for an object without calling a constructor:
User u = (User) unsafeInstance.allocateInstance(User.class);In this article, we covered the initialization of fields in Java. Then we examined different data types in Java and how to use them. We also explored several ways of creating objects in Java.