Baeldung Pro comes with both absolutely No-Ads as well as finally with Dark Mode, for a clean learning experience:
Once the early-adopter seats are all used, the price will go up and stay at $33/year.
Last updated: January 8, 2024
The two most prevalent modes of passing arguments to methods are “passing-by-value” and “passing-by-reference”. Different programming languages use these concepts in different ways. As far as Java is concerned, everything is strictly Pass-by-Value.
In this tutorial, we’re going to illustrate how Java passes arguments for various types.
Let’s start with some of the different mechanisms for passing parameters to functions:
The two most common mechanisms in modern programming languages are “Pass-by-Value” and “Pass-by-Reference”. Before we proceed, let’s discuss these first:
When a parameter is pass-by-value, the caller and the callee method operate on two different variables which are copies of each other. Any changes to one variable don’t modify the other.
It means that while calling a method, parameters passed to the callee method will be clones of original parameters. Any modification done in callee method will have no effect on the original parameters in caller method.
When a parameter is pass-by-reference, the caller and the callee operate on the same object.
It means that when a variable is pass-by-reference, the unique identifier of the object is sent to the method. Any changes to the parameter’s instance members will result in that change being made to the original value.
The fundamental concepts in any programming language are “values” and “references”. In Java, Primitive variables store the actual values, whereas Non-Primitives store the reference variables which point to the addresses of the objects they’re referring to. Both values and references are stored in the stack memory.
Arguments in Java are always passed-by-value. During method invocation, a copy of each argument, whether its a value or reference, is created in stack memory which is then passed to the method.
In case of primitives, the value is simply copied inside stack memory which is then passed to the callee method; in case of non-primitives, a reference in stack memory points to the actual data which resides in the heap. When we pass an object, the reference in stack memory is copied and the new reference is passed to the method.
Let’s now see this in action with the help of some code examples.
The Java Programming Language features eight primitive data types. Primitive variables are directly stored in stack memory. Whenever any variable of primitive data type is passed as an argument, the actual parameters are copied to formal arguments and these formal arguments accumulate their own space in stack memory.
The lifespan of these formal parameters lasts only as long as that method is running, and upon returning, these formal arguments are cleared away from the stack and are discarded.
Let’s try to understand it with the help of a code example:
public class PrimitivesUnitTest {
@Test
public void whenModifyingPrimitives_thenOriginalValuesNotModified() {
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
// Before Modification
assertEquals(x, 1);
assertEquals(y, 2);
modify(x, y);
// After Modification
assertEquals(x, 1);
assertEquals(y, 2);
}
public static void modify(int x1, int y1) {
x1 = 5;
y1 = 10;
}
}
Let’s try to understand the assertions in the above program by analyzing how these values are stored in memory:
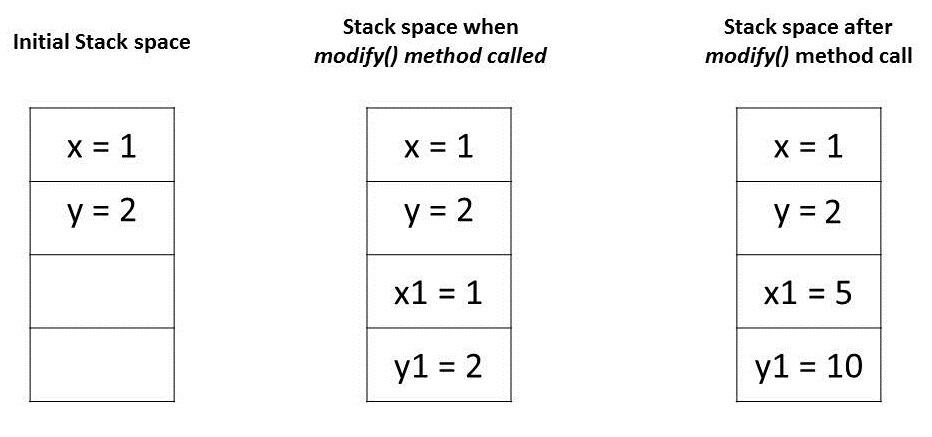
In Java, all objects are dynamically stored in Heap space under the hood. These objects are referred from references called reference variables.
A Java object, in contrast to Primitives, is stored in two stages. The reference variables are stored in stack memory and the object that they’re referring to, are stored in a Heap memory.
Whenever an object is passed as an argument, an exact copy of the reference variable is created which points to the same location of the object in heap memory as the original reference variable.
As a result of this, whenever we make any change in the same object in the method, that change is reflected in the original object. However, if we allocate a new object to the passed reference variable, then it won’t be reflected in the original object.
Let’s try to comprehend this with the help of a code example:
public class NonPrimitivesUnitTest {
@Test
public void whenModifyingObjects_thenOriginalObjectChanged() {
Foo a = new Foo(1);
Foo b = new Foo(1);
// Before Modification
assertEquals(a.num, 1);
assertEquals(b.num, 1);
modify(a, b);
// After Modification
assertEquals(a.num, 2);
assertEquals(b.num, 1);
}
public static void modify(Foo a1, Foo b1) {
a1.num++;
b1 = new Foo(1);
b1.num++;
}
}
class Foo {
public int num;
public Foo(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
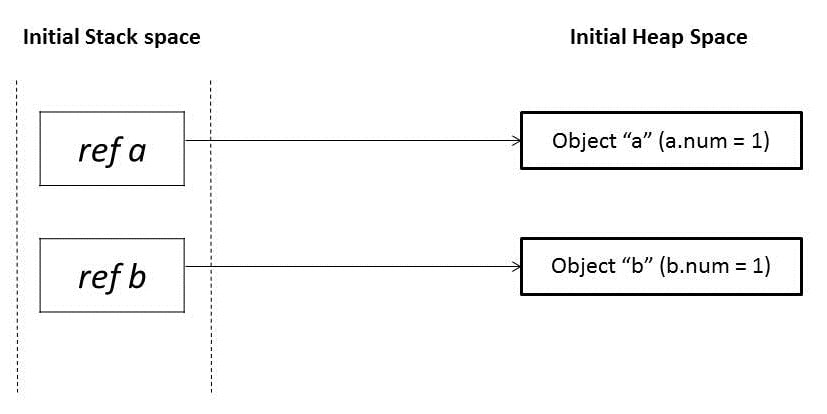
}Let’s analyze the assertions in the above program. We have passed objects a and b in modify() method that has the same value 1. Initially, these object references are pointing to two distinct object locations in a heap space:
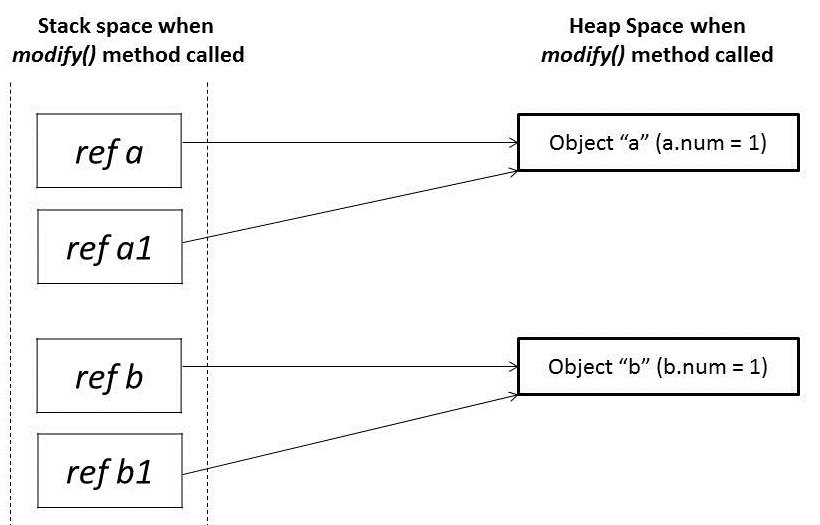
When these references a and b are passed in the modify() method, it creates mirror copies of those references a1 and b1 which point to the same old objects:
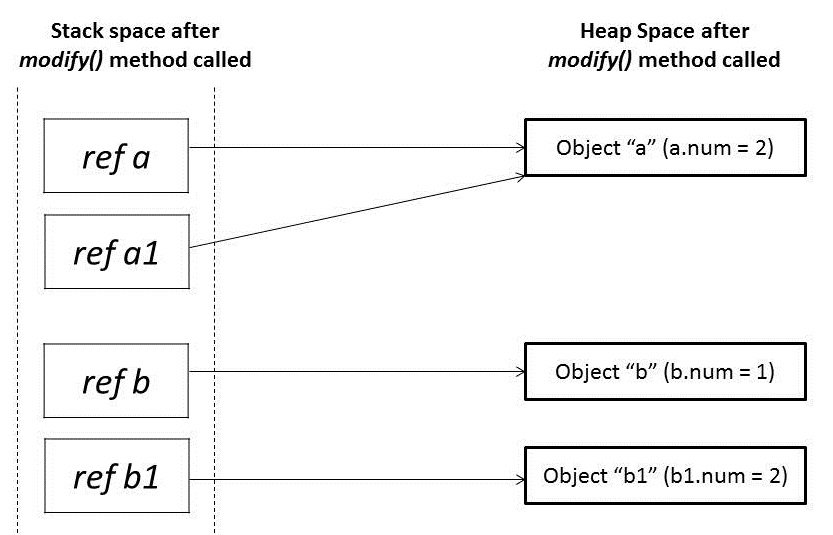
In the modify() method, when we modify reference a1, it changes the original object. However, for a reference b1, we have assigned a new object. So it’s now pointing to a new object in heap memory.
Any change made to b1 will not reflect anything in the original object:
In this article, we looked at how parameter passing is handled in case of Primitives and Non-Primitives.
We learned that parameter passing in Java is always Pass-by-Value. However, the context changes depending upon whether we’re dealing with Primitives or Objects: