Baeldung Pro comes with both absolutely No-Ads as well as finally with Dark Mode, for a clean learning experience:
Once the early-adopter seats are all used, the price will go up and stay at $33/year.
Last updated: April 14, 2024
In this quick tutorial, we’ll learn how to use Liquibase to evolve the database schema of a Java web application. First, we’ll examine a general Java app, and then we’ll focus on some interesting options available that integrate well with Spring and Hibernate.
When using Liquibase, we can describe the evolution of the database schema using a sequence of changelog files. Although these files can be written in many formats, such as SQL, XML, JSON, and YAML, here we’ll focus only on the XML format to describe changes for our DB. So, we can have many changelog files for our DB as we change its schema over time. Additionally, all these files have a reference in a single root changelog file named master.xml, which Liquibase will use.
We can use the include and includeAll attributes to nest other changelog files under this root changelog.
Let’s start by including the latest liquibase-core dependency in our pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.liquibase</groupId>
<artifactId>liquibase-core</artifactId>
<version>4.27.0</version>
</dependency>First, let’s take a look at a simple XML changelog file to understand its structure. For this example, we created a file named 20170503041524_added_entity_Car.xml, which adds a new table called car with id, make, brand, and price as its column:
<databaseChangeLog xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-latest.xsd">
...
<!--Added the entity Car-->
<changeSet id="20170503041524-1" author="user">
<createTable tableName="car">
<column name="id" type="bigint" autoIncrement="${autoIncrement}">
<constraints primaryKey="true" nullable="false" />
</column>
<column name="make" type="varchar(255)">
<constraints nullable="true" />
</column>
<column name="brand" type="varchar(255)">
<constraints nullable="true" />
</column>
<column name="price" type="double">
<constraints nullable="true" />
</column>
</createTable>
</changeSet>
</databaseChangeLog>Let’s ignore all the namespace definitions for a second and focus on the changeSet tag. It’s worth noting how an id and author attributes identify the change set. This ensures that any given change is applied only once. Moreover, we can see directly the author of the change as well.
Now, to use this change log, we need to define that file in the master.xml:
<databaseChangeLog xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-latest.xsd">
<include file="classpath:config/liquibase/changelog/00000000000000_initial_schema.xml" relativeToChangelogFile="false" />
<include file="classpath:config/liquibase/changelog/20170503041524_added_entity_Car.xml" relativeToChangelogFile="false" />
</databaseChangeLog>Now, Liquibase uses the master.xml file to track the changesets that have already been applied to the database. To reduce conflicts, we prepend the file containing the changeset with a data timestamp. The date timestamp allows Liquibase to determine which changesets have already been applied and which still need to be applied. This is just a convention we use and can be changed according to our needs.
Once the changesets are applied, we cannot normally edit the same ones further. So, for any given schema modification, we must create a new changeset file, which will provide consistency in our database versioning.
Let’s now see how to wire this into our Spring application and make sure that it runs when the application starts up.
Our first option to run the changes on application startup is via a Spring bean.
There are, of course, many other ways, but this is a good, simple way to go if we’re dealing with a Spring application:
@Bean
public SpringLiquibase liquibase() {
SpringLiquibase liquibase = new SpringLiquibase();
liquibase.setChangeLog("classpath:config/liquibase/master.xml");
liquibase.setDataSource(dataSource());
return liquibase;
}
Alternatively, a more complete configuration file requires additional settings:
@Bean
public SpringLiquibase liquibase(@Qualifier("taskExecutor") TaskExecutor taskExecutor,
DataSource dataSource, LiquibaseProperties liquibaseProperties) {
// Use liquibase.integration.spring.SpringLiquibase if you don't want Liquibase to start asynchronously
SpringLiquibase liquibase = new AsyncSpringLiquibase(taskExecutor, env);
liquibase.setDataSource(dataSource);
liquibase.setChangeLog("classpath:config/liquibase/master.xml");
liquibase.setContexts(liquibaseProperties.getContexts());
liquibase.setDefaultSchema(liquibaseProperties.getDefaultSchema());
liquibase.setDropFirst(liquibaseProperties.isDropFirst());
if (env.acceptsProfiles(JHipsterConstants.SPRING_PROFILE_NO_LIQUIBASE)) {
liquibase.setShouldRun(false);
} else {
liquibase.setShouldRun(liquibaseProperties.isEnabled());
log.debug("Configuring Liquibase");
}
return liquibase;
}Again, we create our master.xml file on the project’s classpath. Therefore, if the location differs, we might want to provide the correct path.
When using Spring Boot, we don’t need to define a bean for Liquibase, as including the liquibase-core dependency will do that for us. But we need to put the master.xml specifically in src/main/resources/config/liquibase/master.xml so that Liquibase can read it and run automatically on startup.
Alternatively, we can also change the default changelog file location by setting the spring.liquibase.change-log property:
spring.liquibase.change-log=classpath:liquibase-changeLog.xmlSometimes, we might not want to run Liquibase migration on startup. So, to disable Liquibase, we can use spring.liquibase.enabled property:
spring.liquibase.enabled=falseThis way, Liquibase configurations are not applied, and the schema of the database stays the same.
We should keep in mind that applications before Spring Boot 2.x, required the use of liquibase.enabled property:
liquibase.enabled=falseWriting changelog files manually can be time-consuming and error-prone. Instead, we can use the Liquibase Maven plugin to generate one from an existing database and save ourselves a lot of work.
Let’s use the latest liquibase-maven-plugin dependency in our pom.xml:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.liquibase</groupId>
<artifactId>liquibase-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>4.27.0</version>
...
<configuration>
...
<driver>org.h2.Driver</driver>
<url>jdbc:h2:file:./target/h2db/db/carapp</url>
<username>carapp</username>
<password />
<outputChangeLogFile>src/main/resources/liquibase-outputChangeLog.xml</outputChangeLogFile>
</configuration>
</plugin>Above, we are just describing the database driver with its related configurations and the output of the change log file.
Let’s use a mvn command to generate a changelog from an existing database:
mvn liquibase:generateChangeLogNow, we can use the resulting changelog file to either create an initial DB schema or to populate data.
This will create a changeLog file in the configured location:
<databaseChangeLog ...>
<changeSet id="00000000000001" author="jhipster">
<createTable tableName="jhi_persistent_audit_event">
<column name="event_id" type="bigint" autoIncrement="${autoIncrement}">
<constraints primaryKey="true" nullable="false" />
</column>
<column name="principal" type="varchar(50)">
<constraints nullable="false" />
</column>
<column name="event_date" type="timestamp" />
<column name="event_type" type="varchar(255)" />
</createTable>
<createTable tableName="jhi_persistent_audit_evt_data">
<column name="event_id" type="bigint">
<constraints nullable="false" />
</column>
<column name="name" type="varchar(150)">
<constraints nullable="false" />
</column>
<column name="value" type="varchar(255)" />
</createTable>
<addPrimaryKey columnNames="event_id, name" tableName="jhi_persistent_audit_evt_data" />
<createIndex indexName="idx_persistent_audit_event" tableName="jhi_persistent_audit_event" unique="false">
<column name="principal" type="varchar(50)" />
<column name="event_date" type="timestamp" />
</createIndex>
<createIndex indexName="idx_persistent_audit_evt_data" tableName="jhi_persistent_audit_evt_data" unique="false">
<column name="event_id" type="bigint" />
</createIndex>
<addForeignKeyConstraint baseColumnNames="event_id" baseTableName="jhi_persistent_audit_evt_data" constraintName="fk_evt_pers_audit_evt_data" referencedColumnNames="event_id" referencedTableName="jhi_persistent_audit_event" />
</changeSet>
<changeSet id="20170503041524-1" author="jhipster">
<createTable tableName="car">
<column name="id" type="bigint" autoIncrement="${autoIncrement}">
<constraints primaryKey="true" nullable="false" />
</column>
<column name="make" type="varchar(255)">
<constraints nullable="true" />
</column>
<column name="brand" type="varchar(255)">
<constraints nullable="true" />
</column>
<column name="price" type="double">
<constraints nullable="true" />
</column>
<!-- jhipster-needle-liquibase-add-column - JHipster will add columns here, do not remove-->
</createTable>
</changeSet>
</databaseChangeLog>Next, using the diff command, we can generate a changeLog file that contains the differences between two existing databases:
mvn liquibase:diffWe can then use this file to align two databases. For this to work correctly, we need to configure the liquibase plugin with additional properties:
changeLogFile=src/main/resources/config/liquibase/master.xml
url=jdbc:h2:file:./target/h2db/db/carapp
username=carapp
password=
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
referenceUrl=jdbc:h2:file:./target/h2db/db/carapp2
referenceDriver=org.h2.Driver
referenceUsername=tutorialuser2
referencePassword=tutorialmy5ql2Again, this will generate a changeLog file:
<databaseChangeLog ...>
<changeSet author="John" id="1439227853089-1">
<dropColumn columnName="brand" tableName="car"/>
</changeSet>
</databaseChangeLog>This is a super powerful way to evolve our DB. For example, we could allow Hibernate to auto-generate a new schema for development and then use that as a reference point against the old schema.
If our application uses Hibernate, we can use the liquibase-hibernate5 to generate the changeLog file.
First, let’s add the latest version of the dependency in our pom.xml:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.liquibase</groupId>
<artifactId>liquibase-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>4.27.0</version>
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>org.liquibase.ext</groupId>
<artifactId>liquibase-hibernate5</artifactId>
<version>3.6</version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
...
</plugin>Now, we can use this plugin to generate a changelog file based on the differences between an existing database (for example, production) and our new persistence entities.
So, to make things simple, once an entity is modified, we can generate the changes against the old DB schema, getting a clean, powerful way to evolve our schema in production.
Here are the liquibase properties in our plugin configuration inside the pom.xml:
<configuration>
<changeLogFile>src/main/resources/config/liquibase/master.xml</changeLogFile>
<diffChangeLogFile>src/main/resources/config/liquibase/changelog/${maven.build.timestamp}_changelog.xml</diffChangeLogFile>
<driver>org.h2.Driver</driver>
<url>jdbc:h2:file:./target/h2db/db/carapp</url>
<defaultSchemaName />
<username>carapp</username>
<password />
<referenceUrl>hibernate:spring:com.car.app.domain?dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
&hibernate.physical_naming_strategy=org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.hibernate.SpringPhysicalNamingStrategy
&hibernate.implicit_naming_strategy=org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.hibernate.SpringImplicitNamingStrategy
</referenceUrl>
<verbose>true</verbose>
<logging>debug</logging>
</configuration>Notably, the referenceUrl is using package scan, so the dialect parameter is required.
If we’re using a non-Hibernate ORM (e.g., EclipseLink or OpenJPA) or we don’t want to add extra dependencies like the liquibase-hibernate plugin, we can use JPA Buddy. This IntelliJ IDEA plugin integrates useful Liquibase features into the IDE.
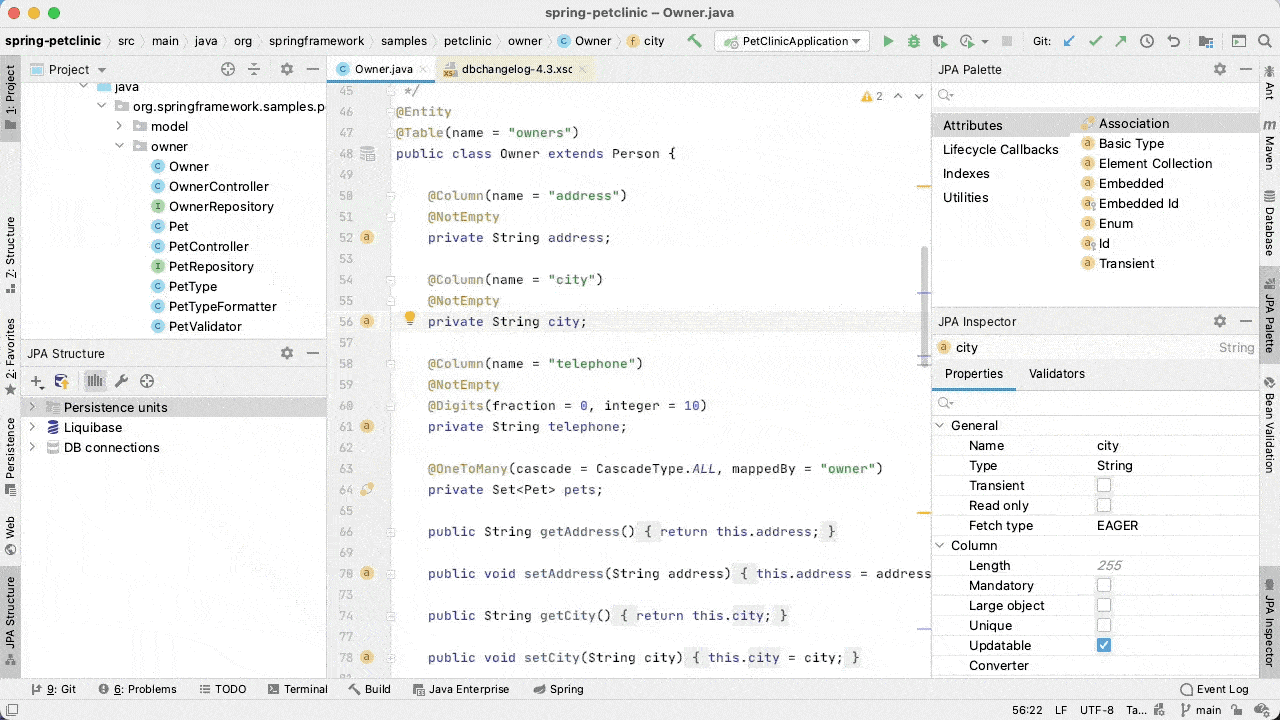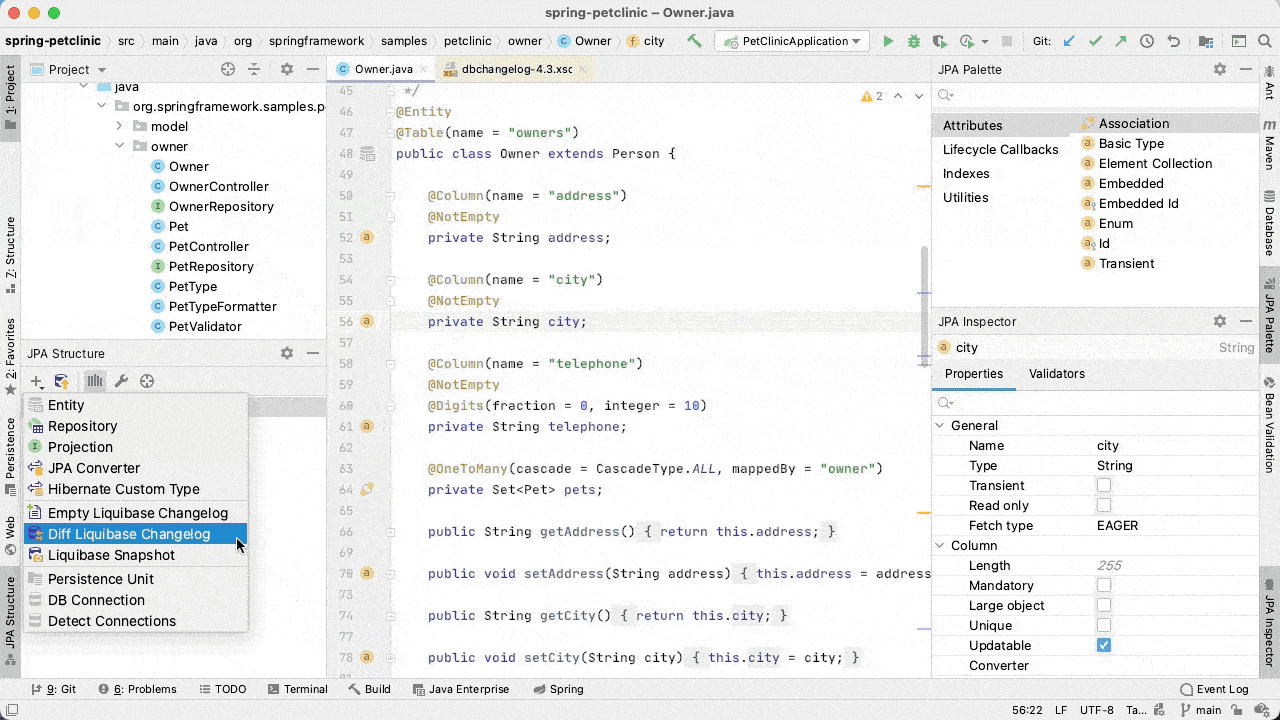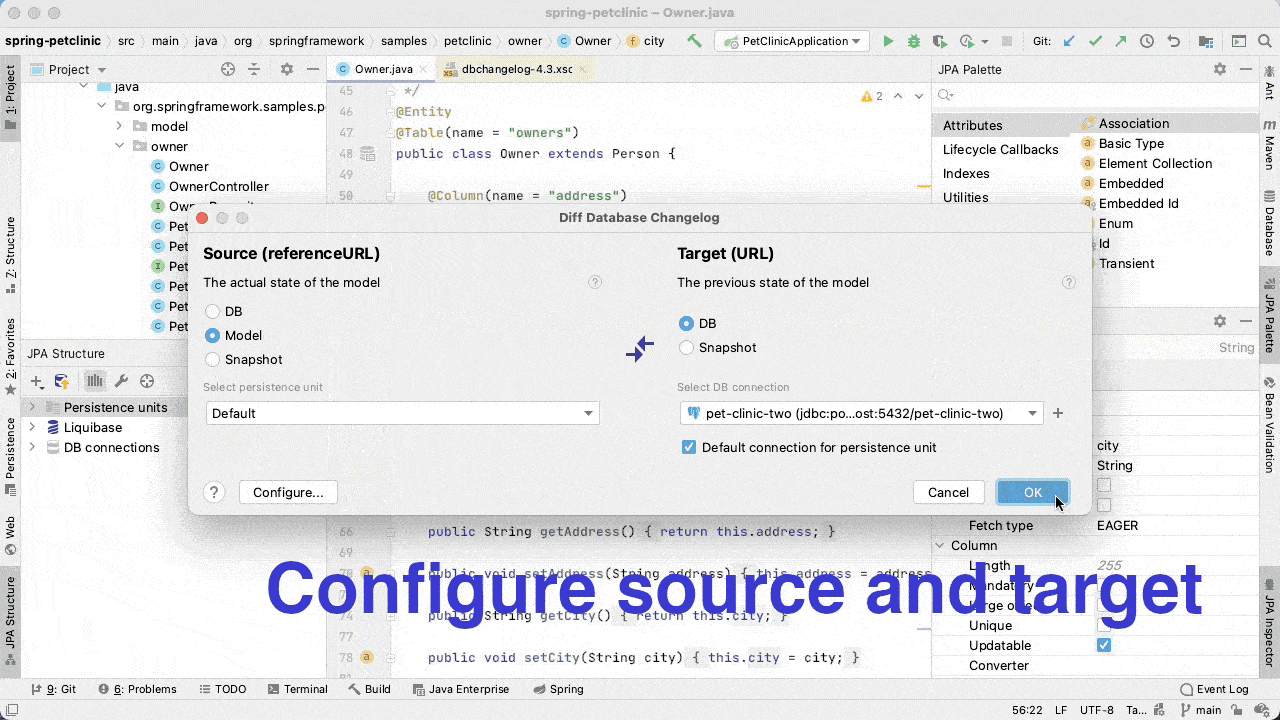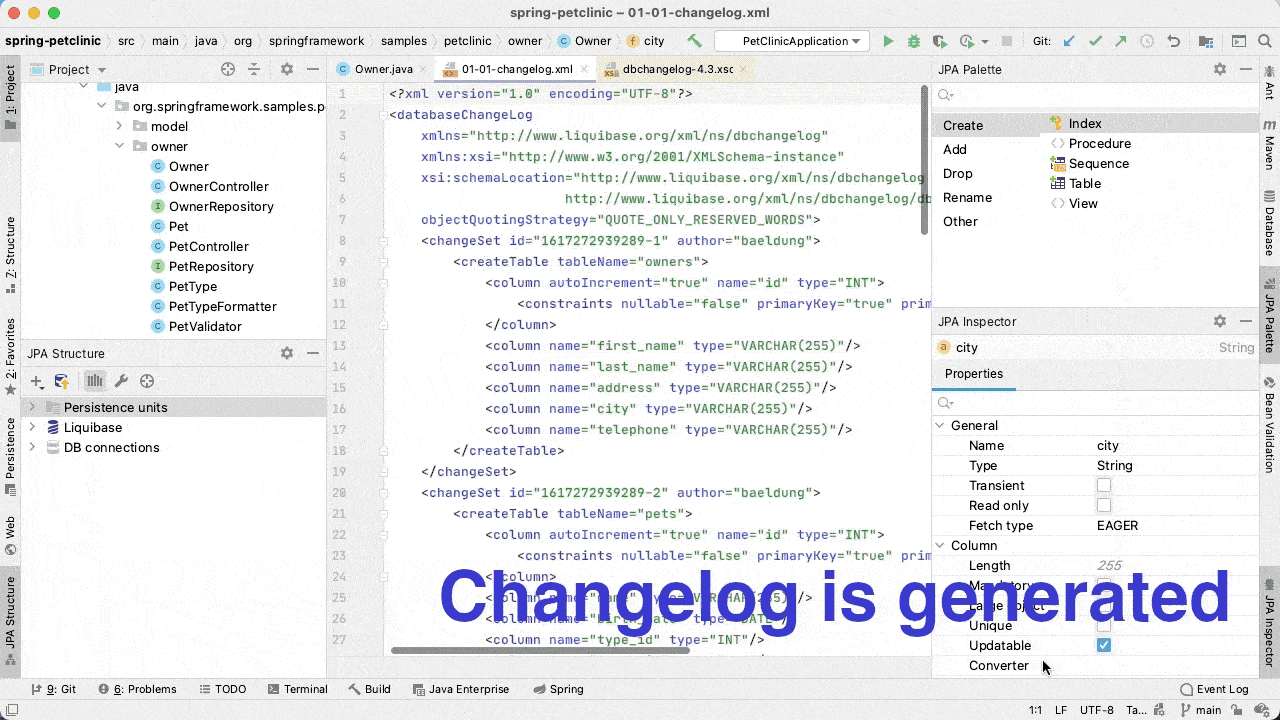
To generate a differential changelog, we install the plugin and then call the action from the JPA Structure panel. We select the source we want to compare (database, JPA entities or Liquibase snapshot) with the target (database or Liquibase snapshot).
JPA Buddy will generate the changeLog as shown in the animation below:
Another advantage of JPA Buddy over the liquibase-hibernate plugin is the ability to override default mappings between Java and database types. Also, it works correctly with Hibernate custom types and JPA converters.
In this article, we illustrated several ways to use Liquibase and get to a safe and mature way of evolving and refactoring the DB schema of a Java app.